Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
🎙️ Listen: Understanding Blockchain Technology: Concepts and Applications
Blockchain technology has emerged as one of the most transformative innovations of our era, impacting various industries beyond its origins in cryptocurrencies. From finance to supply chain management, its potential seems limitless. But what exactly is blockchain technology, and how does it work? This article will provide tech enthusiasts with an in-depth look into blockchain technology, its core concepts, applications, and the future it promises.
“Blockchain is the tech. Bitcoin is merely the first mainstream manifestation of its potential.” – Marc Kenigsberg

At its core, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring that these records cannot be altered retroactively without consensus. It provides transparency, security, and immutability, crucial for creating trust in digital ecosystems.
Blockchain operates on a network of peer-to-peer computers (nodes). Each node stores a copy of the blockchain, validating and storing transaction data in blocks. These blocks are linked together cryptographically, forming an immutable chain. Transactions are validated through consensus algorithms, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
“Everything will be tokenized and connected by a blockchain one day.” – Fred Ehrsam
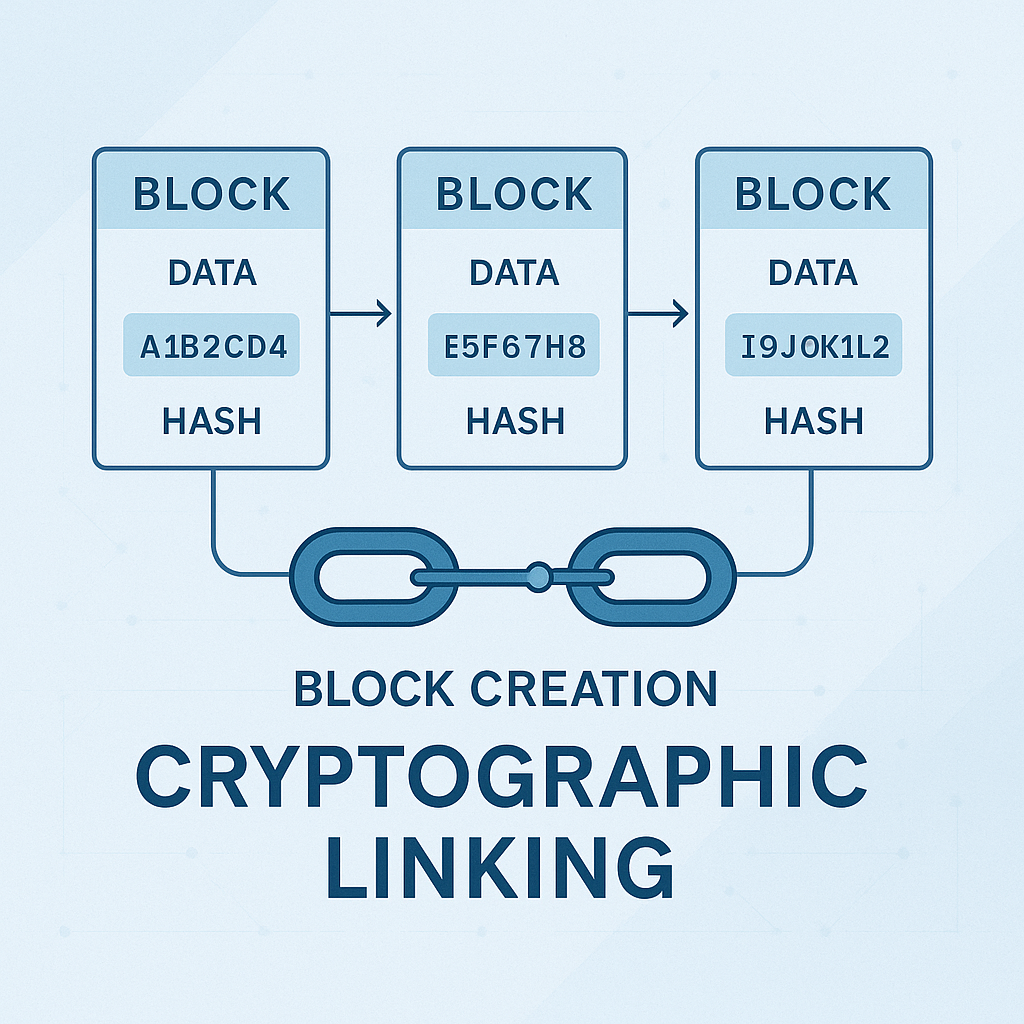
Unlike traditional centralized databases managed by a single authority, blockchain distributes control across the network, reducing points of failure and enhancing security.
Transactions recorded on the blockchain cannot be altered or deleted, providing an accurate historical record, vital for auditing and transparency.
Blockchain networks, especially public blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum, offer transparent transaction histories accessible to anyone, fostering trust.
Cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms secure blockchain transactions, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and cyber-attacks.
Blockchain technology’s versatility means its applications extend well beyond cryptocurrency.
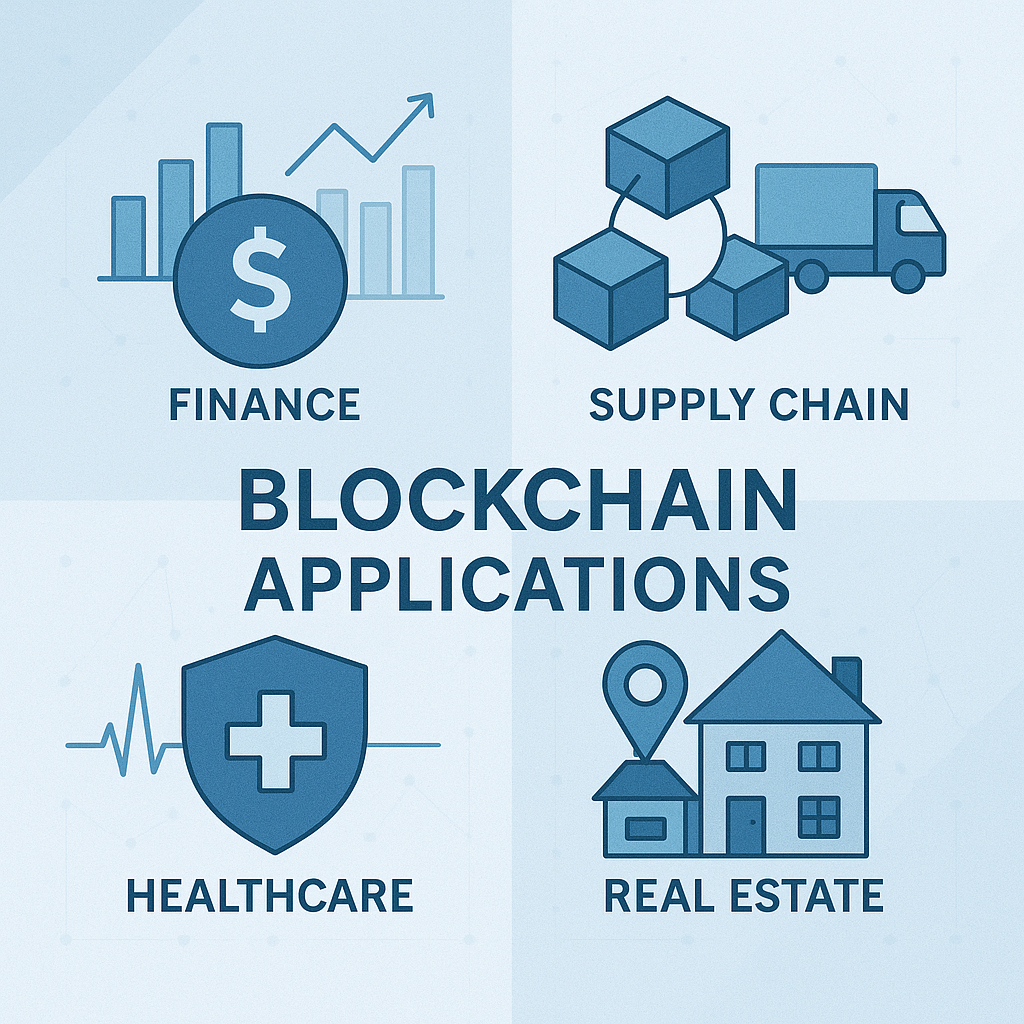
Blockchain enhances transparency, security, and efficiency in financial transactions, facilitating quicker and cheaper cross-border payments, streamlined processes, and improved regulatory compliance.
By tracking goods through every stage of production, shipment, and delivery, blockchain provides unparalleled transparency and traceability, reducing fraud and improving efficiency.
Blockchain technology secures sensitive patient data, ensuring privacy and integrity while enabling seamless data sharing among healthcare providers.
Blockchain simplifies and accelerates property transactions by reducing paperwork, preventing fraud, enabling secure digital contracts (smart contracts), and supporting the tokenization of assets for fractional ownership and increased liquidity.
Companies like Crossmint are developing blockchain platforms that incorporate artificial intelligence to streamline operations and enhance decision-making processes, merging blockchain and AI effectively.
Smart contracts are becoming integral, automating agreements across diverse industries such as insurance, finance, and real estate, significantly reducing manual intervention and disputes.
“Smart contracts, powered by blockchain, will revolutionize the legal, financial, and real estate industries by automating trust.” – Vitalik Buterin
DeFi platforms continue to grow, offering decentralized lending, borrowing, and trading services that challenge traditional financial systems.
Blockchain is increasingly utilized to create secure and verifiable digital identities, enhancing privacy and significantly reducing identity fraud.
Blockchain provides a secure framework for IoT devices to communicate and transact autonomously, improving efficiency and trust in machine-to-machine interactions.
Despite its potential, blockchain technology faces several significant challenges:
Blockchain networks, especially public ones like Ethereum, face issues with transaction speed and scalability, hindering widespread adoption.
Consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work require significant computational resources, raising environmental concerns.
Lack of clear regulations creates ambiguity, deterring businesses from fully adopting blockchain technology.
While blockchain is generally secure, concerns about the safety of smart contracts, hacking vulnerabilities, and private key management continue to require vigilance.
Blockchain continues to evolve rapidly. Innovations like Layer 2 solutions for scalability, sustainable consensus algorithms, and increased interoperability between blockchains indicate a promising future. Industries are increasingly adopting blockchain to enhance efficiency, transparency, and security, making it a pivotal technology for the future.
“Blockchain is not just a technology, it’s a fundamental shift in the way we approach trust, transparency, and collaboration.” – Don Tapscott
Blockchain technology represents a revolutionary shift toward decentralization, transparency, and secure digital transactions. While it faces challenges, ongoing innovations continue to address these concerns, expanding its adoption across various sectors. Understanding blockchain technology is crucial for tech enthusiasts looking to stay ahead in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Wikipedia: Blockchain
Interested in exploring blockchain technology further? Join the conversation and share your thoughts or experiences in the comments below!